ReAct Agent에서의 Tool의 역할

LangChain에서 Agent를 “생각만 하는 존재”가 아니라 “실제로 행동하는 존재”로 만들어주는 핵심 요소가 바로 Tool이다.
ReAct 구조에서 Agent는 다음 과정을 반복한다.
- Reasoning: 무엇을 해야 할지 추론한다
- Action: Tool을 호출하거나 직접 답변한다
- Observation: Tool 실행 결과를 확인한다
ReAct 패턴에서 Tool은 Action, 그리고 그 실행 결과는 Observation에 해당한다.
즉, Tool은 Agent가 실제 세계와 상호작용할 수 있는 유일한 통로다.
- 계산 / 데이터베이스 조회 / 외부 API 호출 / 파일 읽기 및 쓰기
이 모든 것이 Tool을 통해 이루어진다.
가장 기본적인 Tool 정의 : 계산기 예제
먼저 간단한 실수 계산 기 Tool을 정의해보자.
from typing import Literal
from langchain.tools import tool
@tool
def real_number_calculator(
a: float,
b: float,
operation: Literal["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]
) -> float:
"""Perform basic arithmetic operations on two real numbers."""
print("🧮 Invoking calculator tool")
if operation == "add":
return a + b
elif operation == "subtract":
return a - b
elif operation == "multiply":
return a * b
elif operation == "divide":
if b == 0:
raise ValueError("Division by zero is not allowed.")
return a / b
여기서 중요한 점은 다음과 같다.
- 함수 이름은 Tool의 이름으로 사용된다. (여기서는 real_number_calculator)
- docstring은 Tool의 용도를 설명하는 Description이 된다. (Perform basic arithmetic operations on two real numbers.)
- 함수 시그니처(type hint)는 Tool arguments 구조를 정의한다
( a: float / b: float / operation: Literal[...] - 정해진 문자열 중 하나만 허용된다는 의미 )
LLM은 이 정보만 보고 “이 Tool을 언제 써야 할지” 판단한다.

Tool을 사용하는 Agent 만들기
이제 이 Tool을 Agent에 연결한다.
from langchain.agents import create_agent
agent = create_agent(
model="openai:gpt-5",
tools=[real_number_calculator],
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant",
)
Agent를 호출해보면 다음과 같은 흐름이 발생한다.
result = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is 3.1125 * 4.1234"}]}
)
print(result["messages"][-1].content)
---
🧮 Invoking calculator tool
3.1125 × 4.1234 = 12.8340825
Agent는 스스로 판단해 계산기 Tool을 호출하고, Tool의 반환값을 Observation으로 받아 최종 답변을 생성한다.
LangSmith Observability를 보면 다음 정보들을 확인할 수 있다.
- 어떤 Tool이 호출되었는지
- 어떤 argument로 호출되었는지
- Tool 호출 시점과 결과
우리는 Langsmith Observability를 사용해 metadata를 확인할 수 있다.

Tool Description이 중요한 이유
흥미로운 점은, Tool이 항상 호출되는 것은 아니라는 것이다.
예를 들어 다음 질문을 던지면,
result = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is 3 * 4"}]}
)
LLM은 “이 계산은 직접 해도 된다”고 판단해 Tool을 호출하지 않을 수도 있다.
혹은 integer의 계산을 위해 real_number_calculator를 사용해야 한다고 판단하지 않을 수도 있다.
이처럼, Tool 호출 여부는 전적으로 LLM의 판단에 달려 있다.
그리고 이 판단에 가장 큰 영향을 미치는 것이 바로 Tool Description이다.
더 나은 Tool 설계: 상세한 Description 추가
LLM이 Tool을 더 적극적으로 사용하도록 유도하려면, Tool에 더 명확하고 강한 설명을 제공할 수 있다.
@tool(
"calculator",
parse_docstring=True,
description=(
"Perform basic arithmetic operations on two real numbers. "
"Use this whenever you have operations on any numbers, "
"even if they are integers."
),
)
def real_number_calculator(
a: float,
b: float,
operation: Literal["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]
) -> float:
"""Perform basic arithmetic operations on two real numbers.
Args:
a (float): The first number.
b (float): The second number.
operation (Literal["add", "subtract", "multiply", "divide"]):
The arithmetic operation to perform.
Returns:
float: The numerical result.
"""
print("🧮 Invoking calculator tool")
...이 개선된 버전의 핵심은 다음과 같다.
- Tool 이름을 직관적인 "calculator"로 변경
- parse_docstring=True로 argument 설명을 자동 추출
- 정수 입력이어도 Tool을 사용하라고 명시적으로 지시
위 경우 동일한 질문을 던지면, Agent가 훨씬ㄴ 안정적으로 Tool을 호출할 수 있게 된다.
MCP(Model Context Protocol): Agent를 외부 도구 생태계로 확장하기
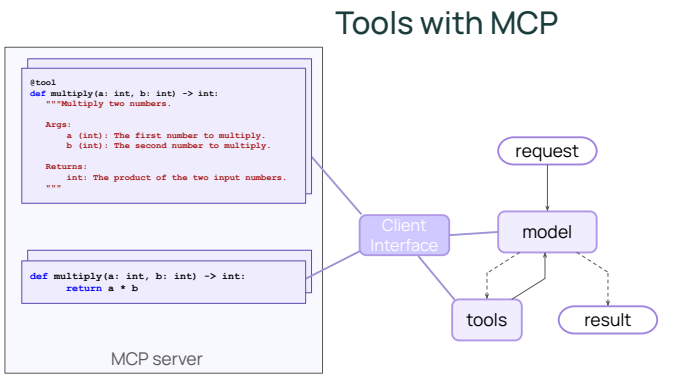
여기서 MCP(Model Context Protocol)는 AI Agent가 외부 Tool과 Application에 접근하는 방식을 표준화하기 위한 개방형 인터페이스로, 기존 LangChain의 Tool 시스템이 “Python 함수 기반 도구 호출”에 초점을 맞췄다면, MCP는 이를 언어·런타임·프로세스를 초월한 도구 호출 규약으로 확장한다.
핵심 아이디어는 단순하다.
Agent는 더 이상 로컬 Python 함수만 호출하지 않고, 별도의 MCP 서버가 제공하는 도구를 마치 로컬 Tool처럼 사용할 수 있다.
MCP의 동작 방식
MCP의 전체 흐름은 LangChain의 기존 Tool 메커니즘과 매우 유사하지만, 실행 주체가 다르다.
- MCP 서버는 자신이 제공하는 Tool 목록과 Description을 외부에 공개한다.
- LangChain Agent는 MCP client를 통해 이 Tool metadata를 받아온다.
- 모델은 기존과 동일하게 Tool Description을 보고 “어떤 Tool을 사용할지” 판단한다.
- Tool 실행 시, 로컬 Tool node가 아니라 MCP 서버로 실행 요청이 전달된다.
- MCP 서버에서 Tool이 실행되고, 그 결과가 Agent로 반환된다.
즉, Reasoning과 Tool 선택은 여전히 LLM이 담당하지만, 실제 Action은 외부 MCP 서버에서 수행된다는 점이 가장 큰 차이다.
LangChain에서 MCP 서버 연결하기
LangChain에서는 langchain-mcp-adapters 패키지를 통해 MCP 서버를 쉽게 연결할 수 있다.
아래 예제에서는 공개된 mcp-time 서버를 사용해 시간 관련 Tool을 로드한다.
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
import nest_asyncio
nest_asyncio.apply()
mcp_client = MultiServerMCPClient(
{
"time": {
"transport": "stdio",
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y", "@theo.foobar/mcp-time"],
}
},
)
mcp_tools = await mcp_client.get_tools()
print(f"Loaded {len(mcp_tools)} MCP tools: {[t.name for t in mcp_tools]}")
---
Loaded 5 MCP tools: ['add_time', 'compare_time', 'convert_timezone', 'current_time', 'relative_time']
이 과정에서 중요한 점은 다음과 같다.
- MCP 서버는 Node.js, Go 등 어떤 언어로 작성되었든 상관없다.
- Agent 입장에서는 “외부 Tool”인지 “로컬 Tool”인지 구분하지 않는다.
- Tool의 이름, 설명, argument 구조는 MCP 서버가 제공한 metadata를 그대로 사용한다.
MCP Tool을 사용하는 Agent 생성
MCP에서 로드한 Tool들은 일반 Tool과 동일하게 create_agent에 전달할 수 있다.
from langchain.agents import create_agent
agent_with_mcp = create_agent(
model="openai:gpt-5-mini",
tools=mcp_tools,
system_prompt="You are a helpful assistant",
)
이제 Agent는 시간 조회, 시간대 변환, 상대 시간 계산 등
MCP 서버가 제공하는 모든 기능을 자신의 Action으로 사용할 수 있다.
이제 Agent에게 샌프란시스코의 현재 시간을 물어보자.
result = await agent_with_mcp.ainvoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What's the time in SF right now?"}]}
)
for msg in result["messages"]:
msg.pretty_print()
---
================================[1m Human Message [0m=================================
What's the time in SF right now?
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
Tool Calls:
current_time (call_yv1gmPLMpYFyDOlzfkW2hEVO)
Call ID: call_yv1gmPLMpYFyDOlzfkW2hEVO
Args:
format: 2006-01-02 15:04:05 MST
timezone: America/Los_Angeles
=================================[1m Tool Message [0m=================================
Name: current_time
2025-10-14 08:48:37 PDT
==================================[1m Ai Message [0m==================================
It's 8:48:37 AM PDT in San Francisco right now (2025-10-14, America/Los_Angeles).
Agent는 다음과 같은 과정을 거친다.
- 질문을 이해하고 “시간 조회”가 필요하다고 판단한다.
- MCP time server가 제공하는 Tool을 선택한다.
- MCP 서버로 실행 요청을 보낸다.
- 서버에서 계산된 시간 결과를 받아 Observation으로 처리한다.
- 최종 AIMessage로 자연스러운 답변을 생성한다.
MCP의 활용 가능성
MCP는 Agent를 단순한 코드 실행 환경에서 해방시킨다.
- Tool을 Python 코드에 묶어둘 필요가 없다.
- 여러 팀, 여러 언어로 작성된 Tool을 하나의 Agent에서 통합할 수 있다.
- 표준화된 인터페이스 덕분에 Tool 배포와 재사용이 쉬워진다.
결과적으로 MCP는 Agent를 로컬 함수 호출기에서, 분산된 도구 생태계의 오케스트레이터로 확장하는 핵심 기술이라고 볼 수 있다.
앞으로 Agent가 실제 서비스와 깊이 연결될수록, MCP는 사실상 “외부 세계와 연결되는 기본 레이어”가 될 가능성이 크다.
'Agentic AI 구축 > LangChain & LangGraph' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [LangChain 함수 6] Agent로 구조화된 출력 생성하기 (0) | 2026.01.10 |
|---|---|
| [LangChain 함수 5] Agent에 Memory 추가하기 (0) | 2026.01.10 |
| [LangChain 함수 3] Streaming을 통해 결과 반환반기 (stream) (0) | 2026.01.10 |
| [LangChain 함수 2] Agent의 Model과 Message 이해하기 (0) | 2026.01.10 |
| [LangChain 함수 1] create_agent 함수 사용 방법 (create_tool_calling_agent Deprecated) (0) | 2026.01.09 |